2025.10.16

Mitsubishi UBE Cement Corporation Advances Black Pellet Business
Joint Business Feasibility Study with Kobe Steel launched to Further Accelerate Carbon Neutrality (CN)

Since 2019, Mitsubishi UBE Cement Corporation has been using its proprietary technology to manufacture black pellets, a type of biomass fuel. In May 2025, it began exploring the possibility of joint business opportunities with Kobe Steel, Ltd. What are the advantages of accelerating the black pellet business?
Mitsubishi UBE Cement Corporation (hereinafter “MUCC”) is investigating the possibilities of a business for black pellets—a biomass energy source currently under the spotlight.
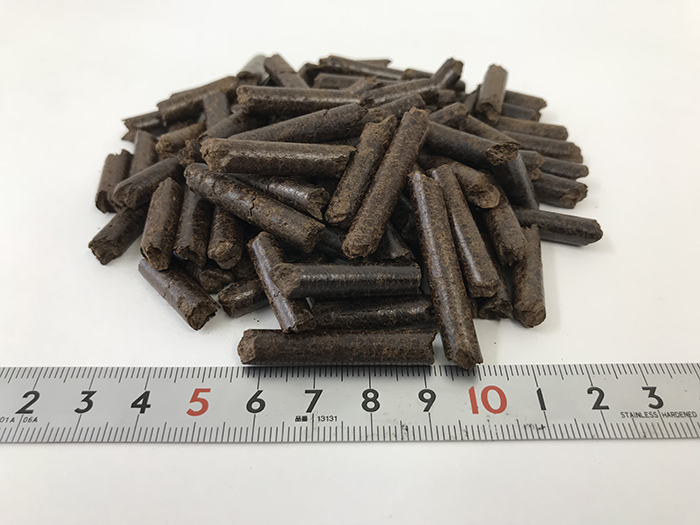
Black pellets are produced by carbonizing wood pellets (white pellets)—a commonly used biomass fuel in Japan—under specific conditions to create a fuel that has a calorific value comparable to coal. The company uses its unique technology to commercialize the fuel under the name MUCC Torrefied Pellets®, and is exploring its potential as an environmentally friendly biomass alternative to coal that can be burned in thermal power plants and other facilities.
MUCC has been manufacturing black pellets since 2019, using the entire output at its own power plants. In May 2025, it announced a feasibility study on a joint black pellet business with Kobe Steel, Ltd. (hereinafter “Kobe Steel”). Kobe Steel is considering using black pellets as raw material for steelmaking as well as for power generation, indicating a potential expansion in MUCC’s black pellet business.
Wataru Hashimoto is a manager in Planning Office and Renewable Energy Project Office, Energy Planning Dept., Environment and Energy Div. for MUCC. He explains:
“The role of these black pellets is to replace coal as fuel. Currently, we manufacture black pellets from white pellets imported from North America using technology we have developed. Our production scale is among the largest in Japan, and we have about five years of operational experience. Taking advantage of our manufacturing technology, we will increase its use at our own power plants first. Looking ahead, we will explore the possibility of marketing the pellets to customers nationwide.”
Advantage of Black Pellets as a Biomass Fuel
Biomass fuels come from natural resources, including wood, agricultural residues, and food waste. Unlike fossil fuels, they are recognized as a renewable energy source. Although they emit CO2 during combustion, they are identified as “carbon neutral” because the plants absorb CO2 through photosynthesis during their growth cycle, resulting in a net zero CO2 emission balance. Historically, MUCC has extensive experience with coal, and this background with solid fuels has driven the company to actively pursue the development of an environmentally friendly solid biomass fuel.
Standard wood pellets and MUCC Torrefied Pellets® comparison
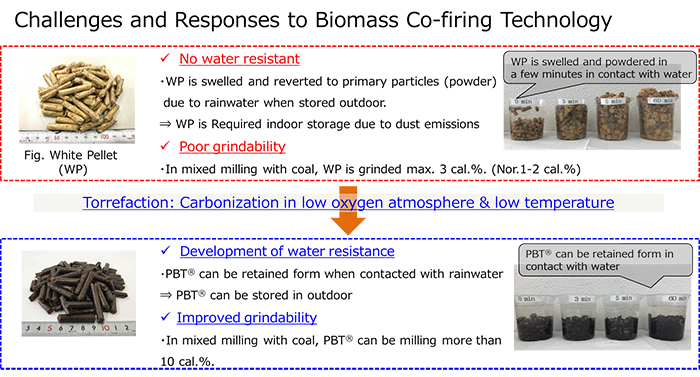
What are the properties of a black pellet? This solid fuel is produced by thermal treatment (torrefaction) of wood biomass at a relatively low temperature in a low oxygen atmosphere. The result is a carbon-neutral fuel with significantly improved water resistance and better grindability compared to non-torrefied wood pellets (white pellets).
How different are black pellets from white pellets? White pellets lack water resistance. As they swell and return to powder form in the rain, they require indoor storage. They don’t pulverize well; when pulverized with coal, only a small percent can be pulverized, and only one to two calories percentage can be used in practice, resulting in a low co-firing ratio.
On the other hand, black pellets are water-resistant. They maintain their shape without disintegrating into powder when exposed to rain, allowing them to be stored in the open air. Furthermore, they have proven to be thoroughly pulverized in coal mills and successfully co-fired at power plants at rates exceeding 10% on a heat input basis.
“Additionally, our operational track record has demonstrated that it’s easier to prevent and manage such risks as spontaneous combustion with black pellets compared to white pellets. This enables us to operate with lower risk and higher safety,” says Hashimoto. “Our black pellet production plant in Ube City, Yamaguchi Prefecture, began operations in December 2019, producing 60,000 tonnes annually. The pellets are co-fired with coal at our thermal power plants.”
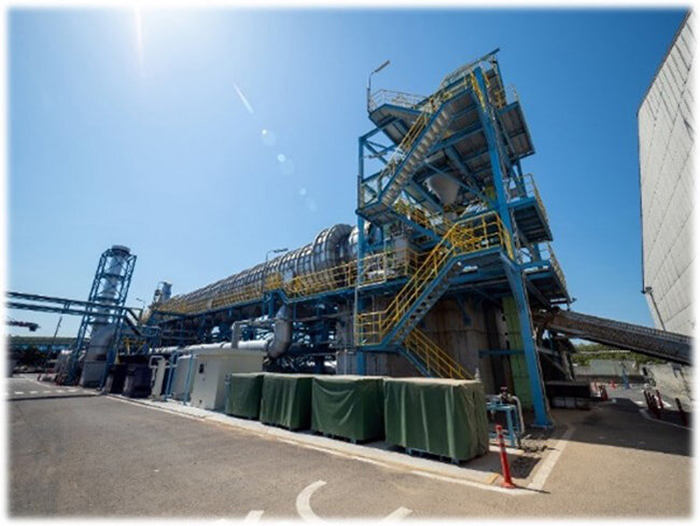

MUCC Torrefied Pellets® Manufacturing Plant in Ube City, Yamaguchi Prefecture
Black Pellets Require Minimal Equipment Investment
Co-firing white pellets with coal at coal-fired power plants required dedicated handling equipment. MUCC Torrefied Pellets® (the brand name for black pellets produced by MUCC) handle like coal, allowing easy co-firing without dedicated wood biomass handling equipment. Because they can be used like conventional coal, companies can introduce the black pellets without upgrading equipment, spending only a small additional investment. Furthermore, these pellets are made from lumber that comes from trees cut for healthy forest development, as well as from inevitable byproducts of the lumbering process, such as scraps, sawdust, and other underutilized timbers. Therefore, they have minimal environmental impact and are considered a carbon-neutral energy resource.
Is the use of black pellets going to increase as a CO2 reduction effort? “Domestically, companies are considering replacing fossil fuels such as coal with new fuels, like hydrogen and ammonia. This is in line with the wider effort to create a carbon-neutral society by 2050,” says Hashimoto. “However, the technical challenges posed by those alternatives remain significant. In this context, I believe that black pellets will increase in popularity as a practical CO2 reduction measure, in particular because they require minimal capital investment.”
Several fuel options exist to achieve CO2 emission reductions. Black pellets are one such option, and they are waiting to make an impact on society.
“We will make this joint initiative the first step of our business expansion,” Hashimoto continues. “Going forward, we will consider adding Southeast Asian white pellets to North American ones to broaden our raw material options while continuing to develop new technologies. We will also strive to improve the black pellet supply system and reduce manufacturing costs. We remain committed to advancing renewable energy development and undertaking initiatives that further contribute to society.”
INTERVIEWEES

Wataru Hashimoto
Manager, Planning Office
Manager, Renewable Energy Project Office
Energy Planning Department, Environment and Energy Division
Mitsubishi UBE Cement Corporation
2-1-1 Uchisaiwaicho, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo
Mitsubishi UBE Cement Corporation, or MUCC, commenced operations in April 2022 after integrating the cement and related businesses of Mitsubishi Materials Corporation and UBE Corporation (the former Ube Industries, Ltd). The company operates in several business fields, including the domestic and international cement, ready-mix concrete, and limestone resource businesses. It is also active in environmental energy-related operations (coal operations, power generation operations, and environmental recycling operations), as well as the building materials business. Its consolidated total of employees is 7,872 (as of March 31, 2025). The group comprises 110 companies.
